A restore of files should always be executed carefully. It is only allowed to do a restore of files to a temporary restore catalog. To set a temporary restore path select userconfiguration and set temporary path restore.
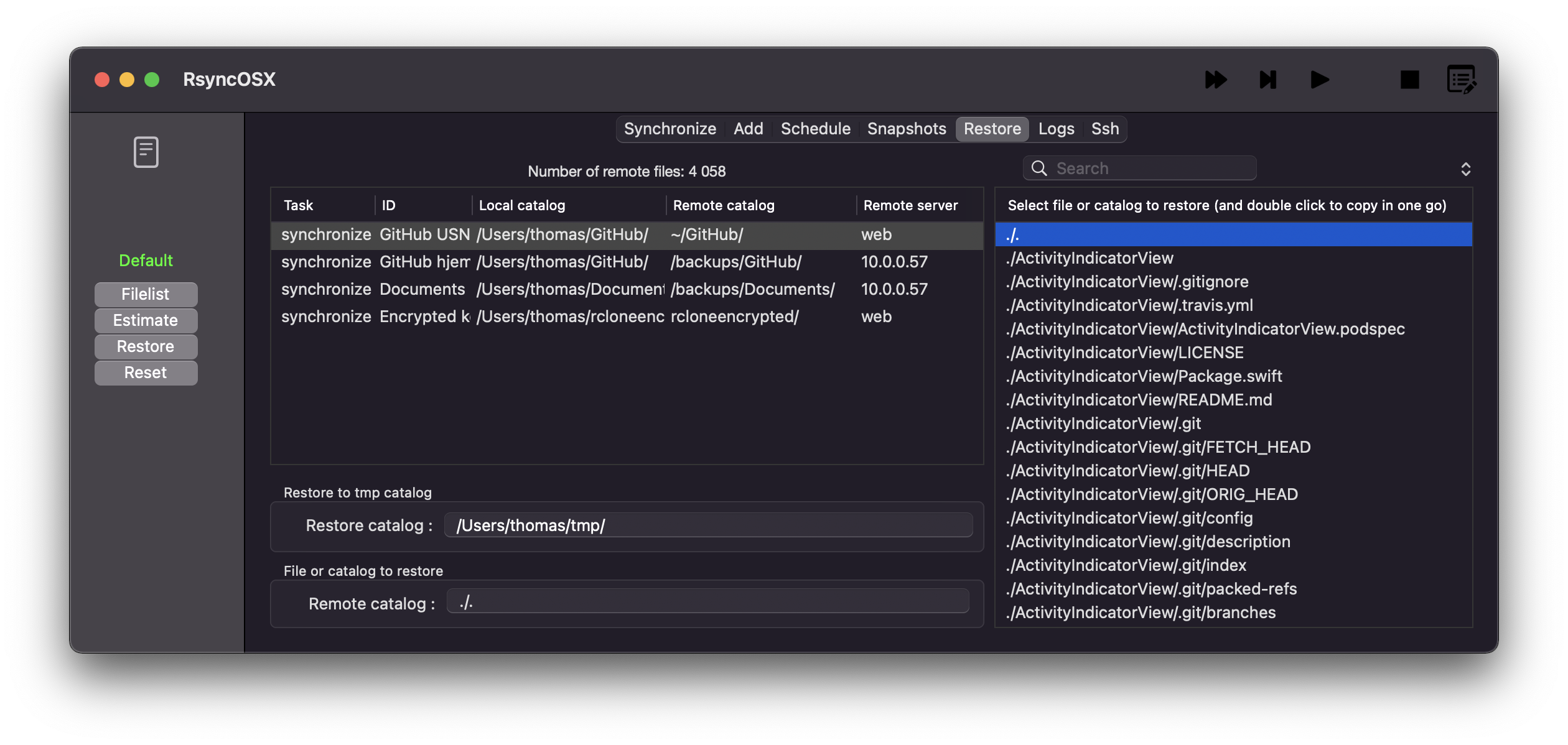
There are two types of restore:
- full restore
- restore by files
- if the remote is a snapshot the list of files might be huge, depends upon how many snapshots and how many files in a snapshot
A restore always start with selecting the task and then the Filelist button. From the list of files either select the ./. or any catalog or file. If the ./. is selected a full restore will be executed.
After selecting do an Estimate and then a Restore.
Restore without estimation
A double click on a file or catalog in the list of files will execute a restore right away.